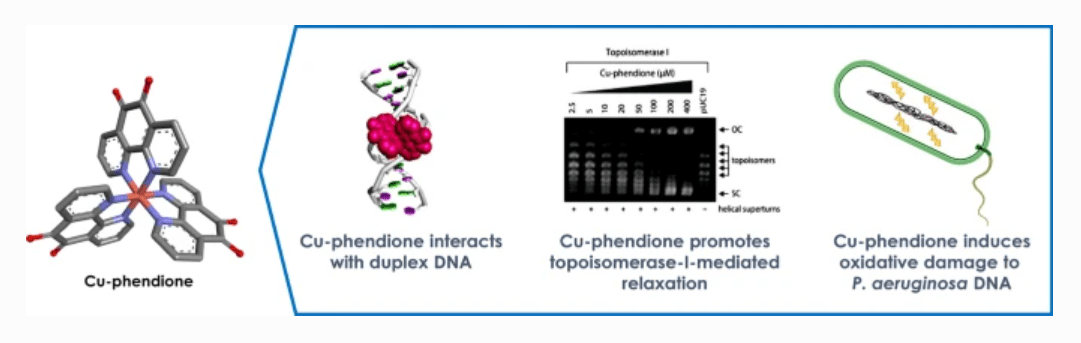
Recent collaborative work from NATURE-ETN has been published in the Journal of Biological Inorganic Chemistry by researchers in the Kellett lab at DCU. Co-authors include NATURE-ETN coordinator Dr. Andrew Kellett, co-supervisor Dr. Georgia Menounou, and ESR Conor Bain. The paper investigated the multi-modal activity of copper(II) and silver(I) complexes with the N,N-coordinating ligand, 1,10-phenanthroline-5,6-dione, with particular focus on DNA damage within Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
The emergence of microbial drug-resistance in recent decades has given rise to the need for novel antimicrobial therapeutics. The metal-based complexes [Ag(1,10-phenanthroline-5,6- dione)2]ClO4 (Ag-phendione) and [Cu(1,10-phenanthroline-5,6-dione)3](ClO4)2.4H2O (Cu-phendione) have previously demonstrated efficient antimicrobial action against multidrug-resistant species. The focus of the study was to understand the binding potential of these complexes with double-stranded DNA using a combination of in silico and in vitro approaches. Promising results arising from this work revealed a potentially new class of antimicrobial drug candidate with a distinct therapeutic mechanism against the multidrug-resistant pathogen P. aeruginosa.
Molecular docking studies showed both complexes elicit a multi-mechanistic approach to DNA-binding via hydrogen bonding, hydrophobic and electrostatic interactions, with both complexes favouring minor groove binding. Of the two complexes, Cu-phendione achieved the highest binding affinity for both major and minor grooves with nearly 10x greater affinity to DNA than Ag-phendione and nearly 20x greater affinity than the phendione ligand alone. Cu-phendione achieved DNA scission through free radical oxidative damage, as well as DNA-nicking and relaxation of supercoiled plasmid DNA. It was concluded that both complexes elicit a dose-dependent effect, with successful DNA fragmentation within multi-drug resistant pathogen P. aeruginosa when treated with a single dose of Cu-phendione. This work proposes a novel dose-regulated class of metal-based antimicrobial therapeutics.
Reference:
Galdino, A.C.M., Viganor, L., Pereira, M.M., Devereux, M., McCann, M., Branquinha, M.H., Molphy, Z., O’Carroll, S., Bain, C., Menounou, G., Kellett, A., Dos Santos, A.L.S. Copper(II) and silver(I)-1,10-phenanthroline-5,6-dione complexes interact with double-stranded DNA: further evidence of their apparent multi-modal activity towards Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Biol Inorg Chem (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00775-021-01922-3